Describe the Two Processes of the Carbon Cycle.
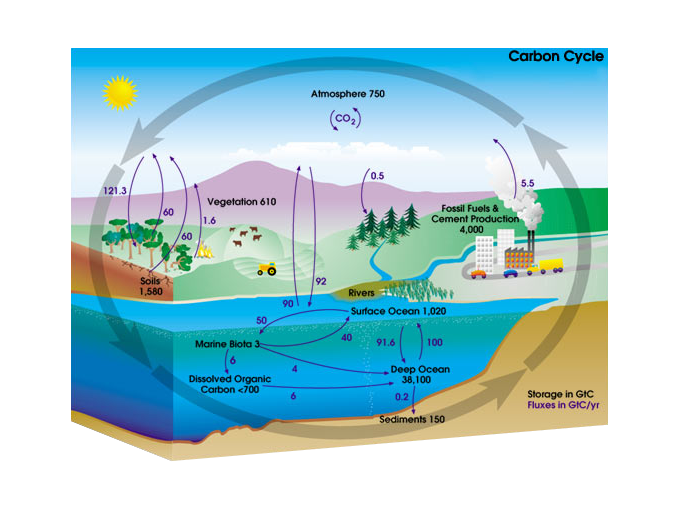
It is stored in what are known as reservoirs and it moves between these reservoirs through a variety of processes including photosynthesis burning fossil fuels and simply releasing breath from the lungs. On average 10 13 to 10 14 grams 10100 million metric tons of carbon move through the slow carbon cycle every year.
What Is The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis Decomposition Respiration And Combustion Earth How
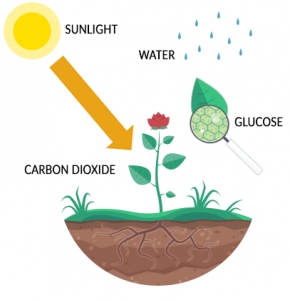
Plants and algaeuse this carbon dioxide along with water and energy from sunlight to produce their own food.

. Carbon enters the atmosphere through natural processes like respiration and industrial applications like burning fossil fuels. It is so named because it only takes days months or years for carbon to flow through the various carbon pools. This means that in terms of a system we are talking about two separate flows here one draining the land biota reservoir the other draining the soil reservoir.
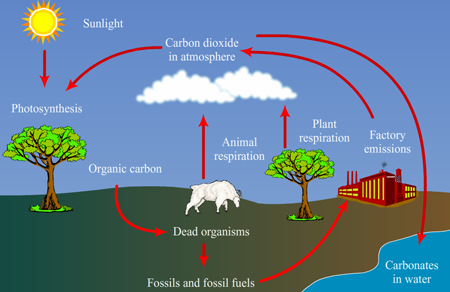
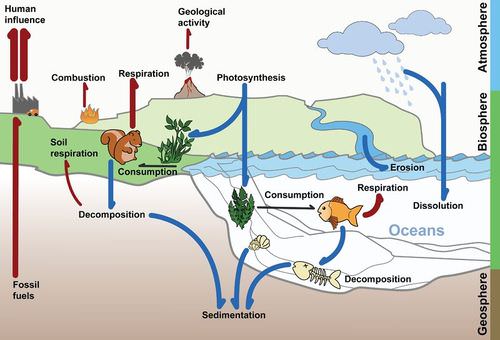
Trees that are burned release CO 2 to the atmosphere via combustion. In one carbon enters a short term cycle when producers convert carbon dioxide in the atmosphere into carbohydrates during photosynthesis when consumers eat the producers they contain carbon from these carbohydrates. Physical oceanography influences the carbon cycle through its modulation of the biology and also through processes that control carbonate chemistry temperature alkalinitysalinity and carbon dioxide flux rates between the air-sea interface surface wind speeds.
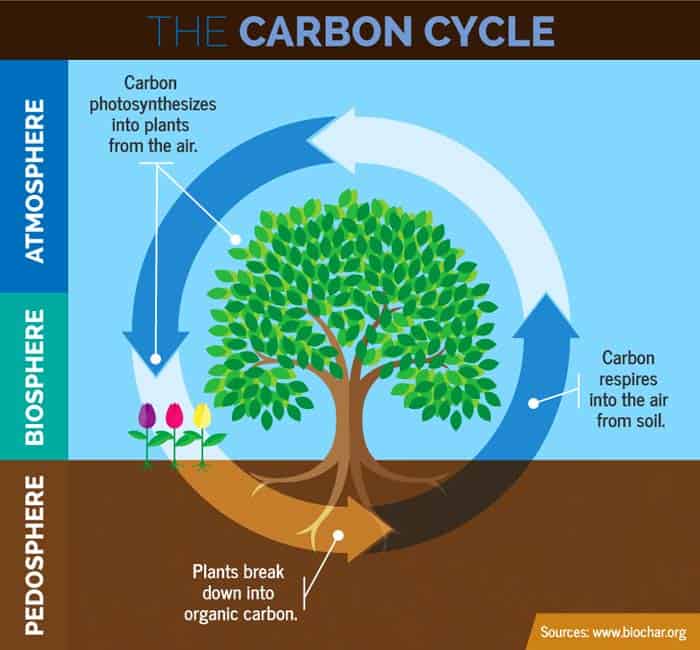
The decomposed plants and animals may then be available as fossil fuel in the. The process of photosynthesis involves the absorption of CO2 by plants to produce carbohydrates. The short term cycling of carbon begins with carbon dioxide and the process of photosynthesis.
The dead organisms dead animals and plants are eaten by decomposers in the ground. The carbon that was in their bodies is then returned to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. The movement of carbon from reservoir to reservoir is known as the carbon cycle.
Both physical and biological processes in the ocean affect the carbon cycle. Prior knowledge questions 1. Which process in living organisms releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
CO 2 is added directly to the atmosphere by animals and some other organisms as a by-product of respiration. Intro to biogeochemical cycles. Carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration and combustion.
Phytoplankton microscopic organisms in the ocean and plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by absorbing it into their cells. Plants and phytoplankton are the main components of the fast carbon cycle. In comparison human emissions of carbon to.
They use energy from the sun to chemically combine carbon dioxide with hydrogen and oxygen from water to create sugar molecules. What is the word equation for aerobic respiration. Describe the two processes of the carbon cycle.
This type occurs during a relatively short period of time. Carbon dioxide is absorbed by producers to make glucose in. Through a series of chemical reactions and tectonic activity carbon takes between 100-200 million years to move between rocks soil ocean and atmosphere in the slow carbon cycle.
Photosynthesis plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and form it into sugar starch and other organic. Trees left behind to decompose emit CO 2 via the process of soil microbial respiration. Processes of Carbon Flow in the Human Realm Fossil Fuel Burning.
They break down the food during cellular respiration releasing the carbon back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. Agriculture for instance involves tilling the soil which leads to very rapid decomposition and oxidation of soil organic matter. Combustion of fossil fuels over a short period of time Why were levels of CO 2 much higher in the atmosphere.
2 Describe the carbon cycle. This type takes thousands of years to appear. Learn how carbon moves through Earths ecosystems and how human activities are altering the carbon cycle.
The other form of human alteration of the global carbon cycle is. How does most carbon get released back into the atmosphere during the geological carbon cycle. Up to 24 cash back The Carbon Cycle Step 4.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Animals that eat plants digest the sugar molecules to get energy for their bodies. Feeding moves carbon in the form of biological molecules along the food chain.
Land-Use Changes -- Forest Burning and Soil Disruption. Up to 24 cash back carbon cycle different from the biological carbon cycle. Respiration excretion and decomposition release the carbon back into the atmosphere or soil continuing the cycle.
The carbon present in animal wastes and in the bodies of all organisms is released as CO 2 by decay or decomposer organisms chiefly bacteria and fungi in a series of microbial transformations. Dead plants and animals C. Find step-by-step Environmental science solutions and your answer to the following textbook question.
Erosion of rocks and minerals D. Both flows transfer carbon to the atmosphere. Processes involved in the carbon cycle are.
Using energy from the Sun both plants and plankton combine carbon dioxide CO 2 and water to form sugar CH 2 O and oxygen. The carbon cycle can be divided into two types according to the duration of the process. Carbon Cycle Processes relavant for timescales of a few hundred years Processes of Flow in the Terrestrial Realm Photosynthesis Plant Respiration Litter Fall and Below-Ground Addition Soil Respiration Runoff Processes of Flow in the Oceanic Realm.
Molecular oxy- gen O 2 is released as an important by-product of this reaction see Chapter 7. The overall stoichiometry of photosynthesis can be expressed as. Which process in living organisms removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
In some circumstances the process of decomposition is prevented. Carbon is released back into the atmosphere when organisms die volcanoes erupt fires blaze fossil fuels are burned and through a variety of other mechanisms. In what form is carbon in the atmosphere.
In the case of the ocean carbon is continually exchanged between the oceans surface waters and the atmosphere or is stored for long periods of time in the ocean depths. Our atmosphere is mostly made of nitrogen and oxygen but there is a small amount of carbon dioxide in the air too. Agricultural land created from deforested areas emits CO 2 to the atmosphere via increased respiration and diffusion from soil that has been turned over tilled.
The equation is as follows. CO H O CH O O 22 2 2 31 where the simple carbohydrate CH 2 O represents organic carbon formed by this process. Another pathway for carbon to move from the sedimentary rock reservoir to the atmosphere is through.
Carbon Cycle And The Earth S Climate

Solved The Two Major Processes Involved In The Carbon Cycle Are

Carbon Cycle Understanding Global Change
How Does Carbon Cycle Through The Biosphere Socratic
What Is The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis Decomposition Respiration And Combustion Earth How
Carbon Cycle Steps Definition Types Importance Biology Explorer
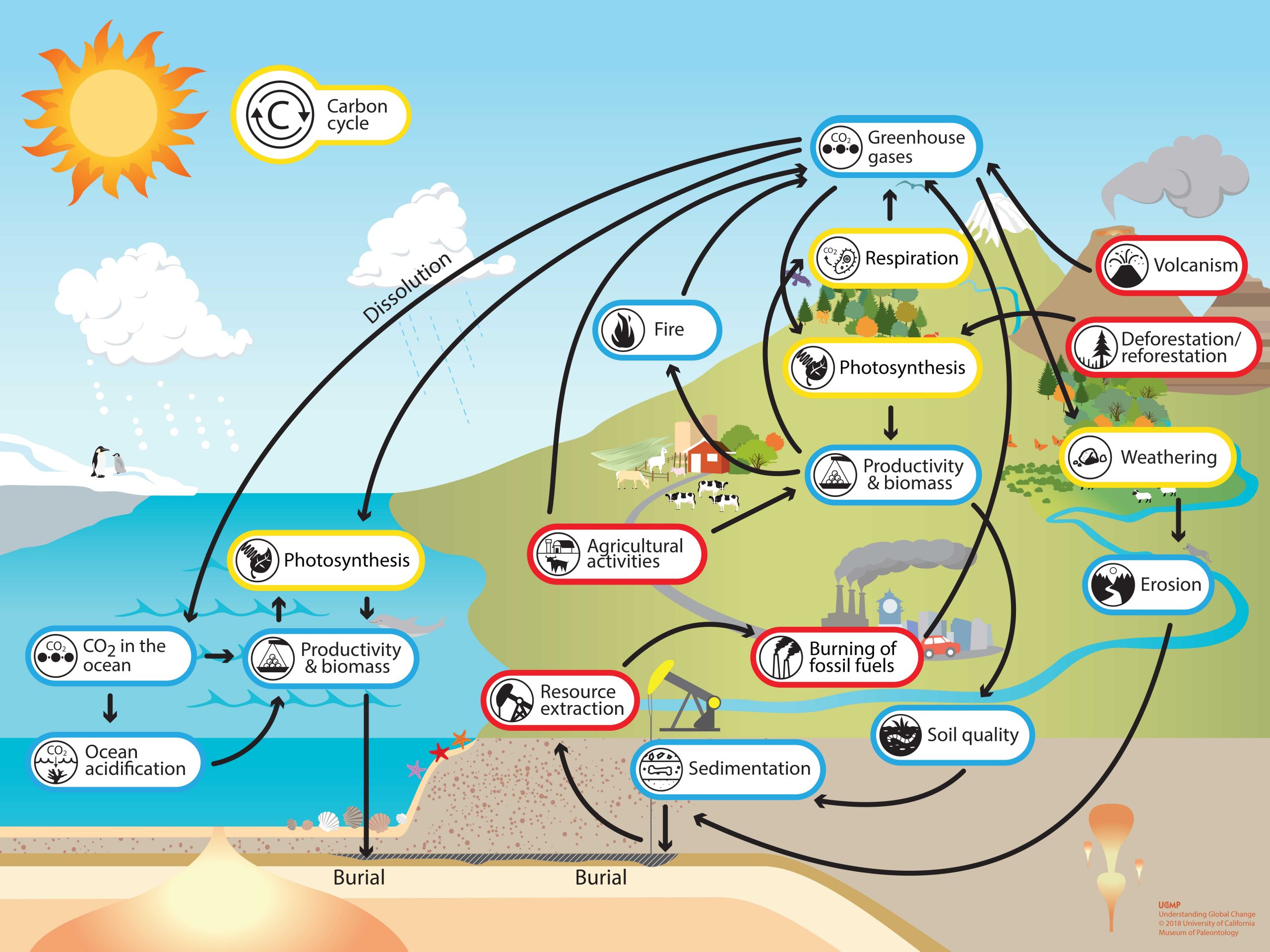
Carbon Cycle Understanding Global Change
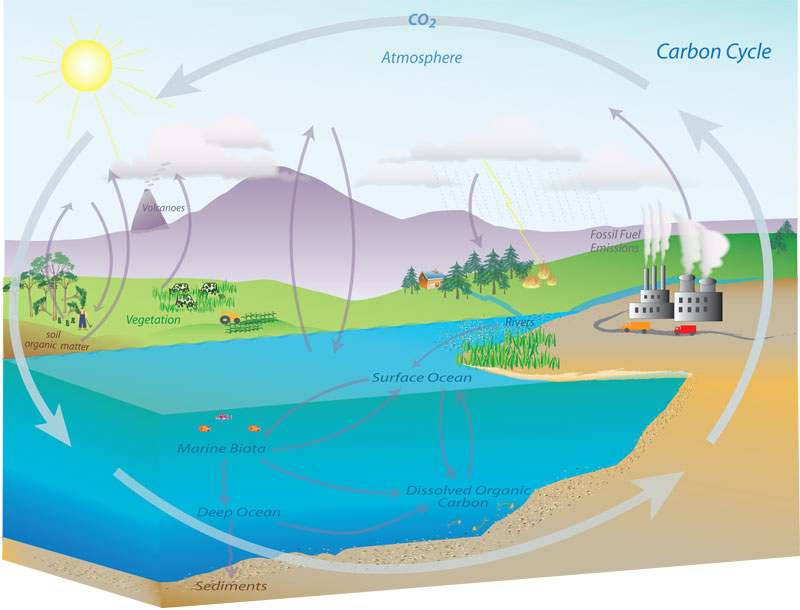
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach

The Carbon Cycle Process Youtube
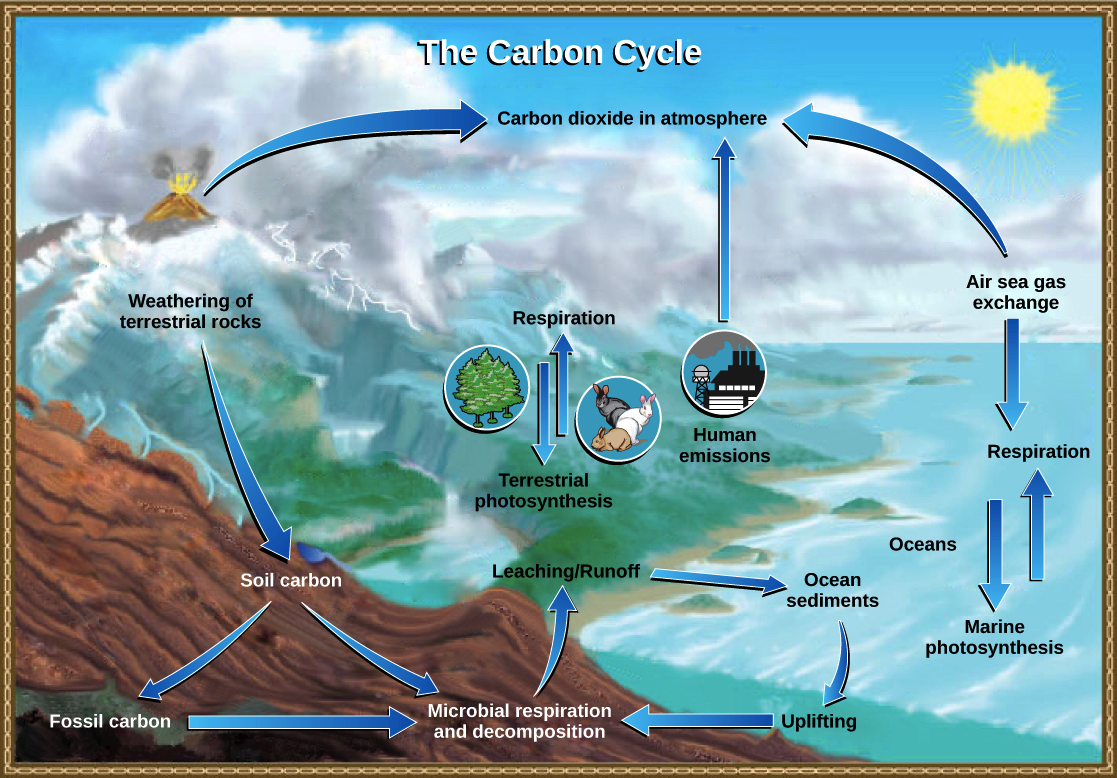
The Carbon Cycle Article Ecology Khan Academy
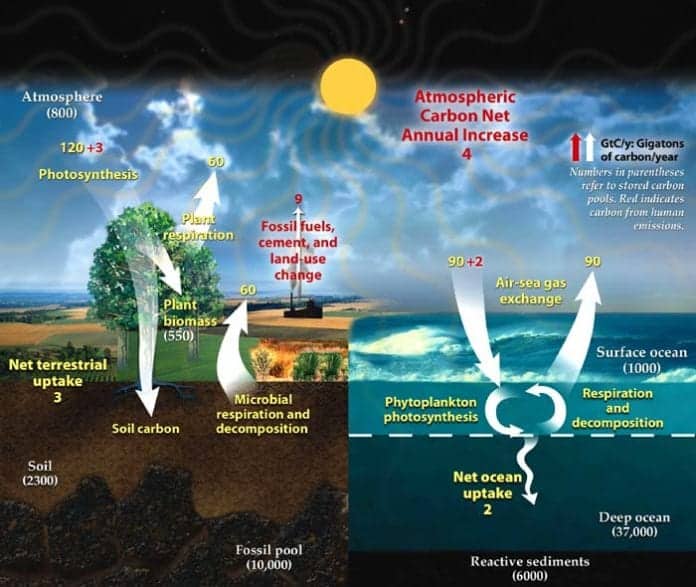
Carbon Cycle Steps Definition Types Importance Biology Explorer
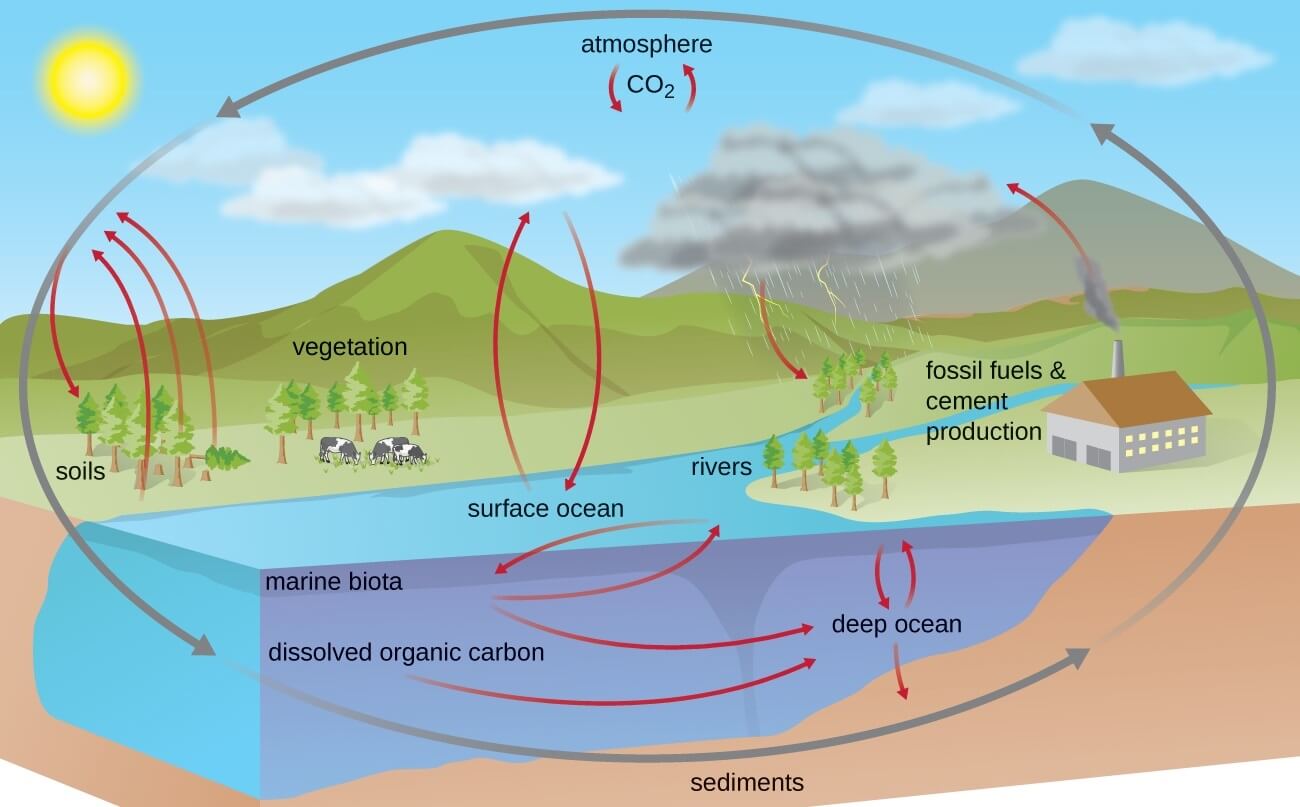
Carbon Cycle Definition Steps Examples Significance Human Impacts

Carbon Cycle Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
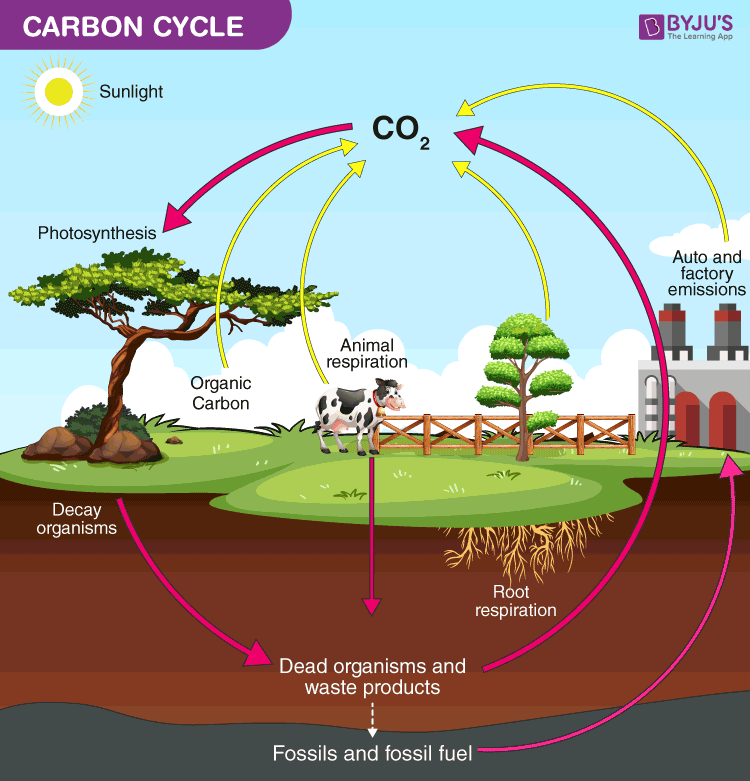
Carbon Cycle Definition Process Diagram Of Carbon Cycle

Carbon Cycle Definition Steps And Examples Biology Dictionary

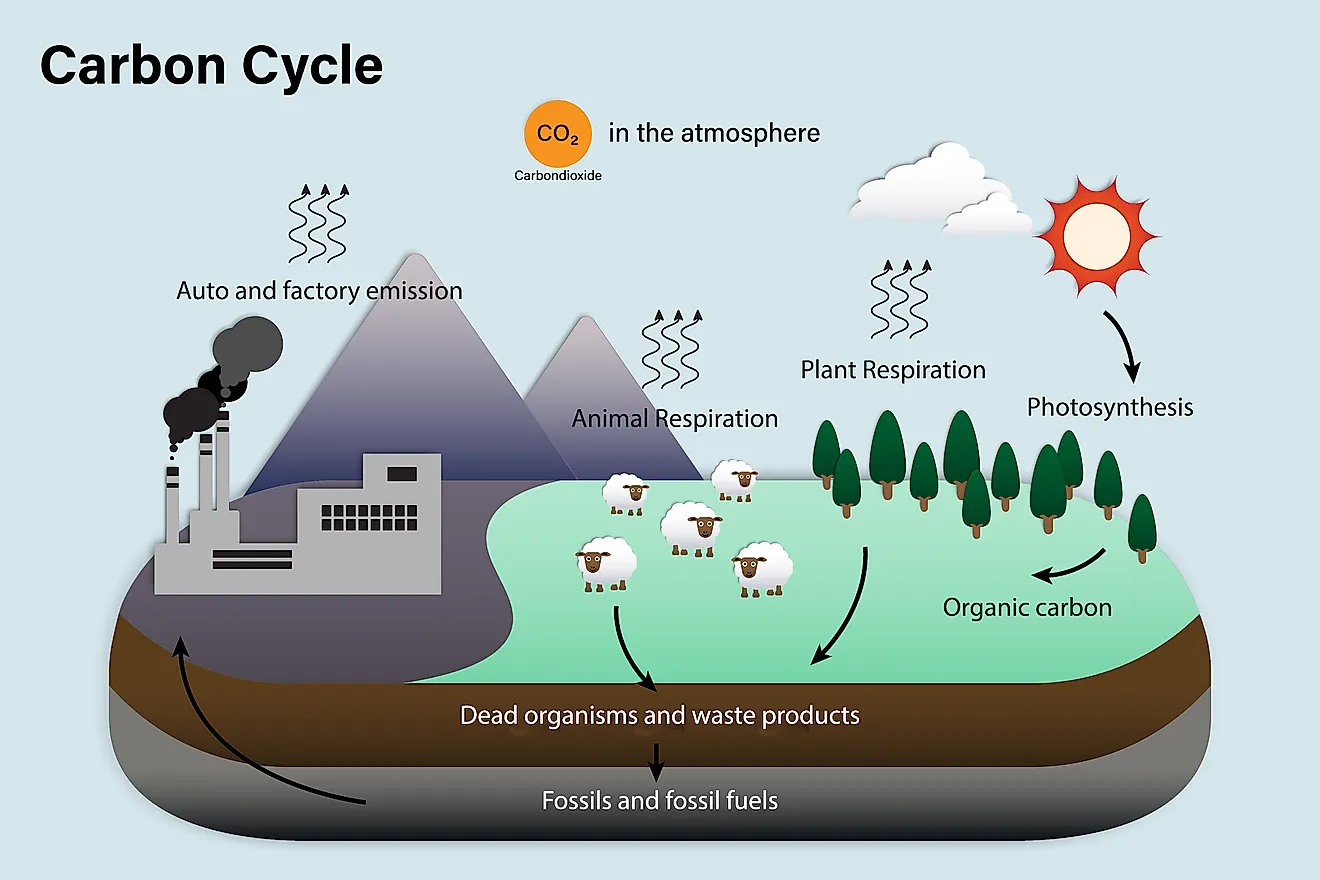
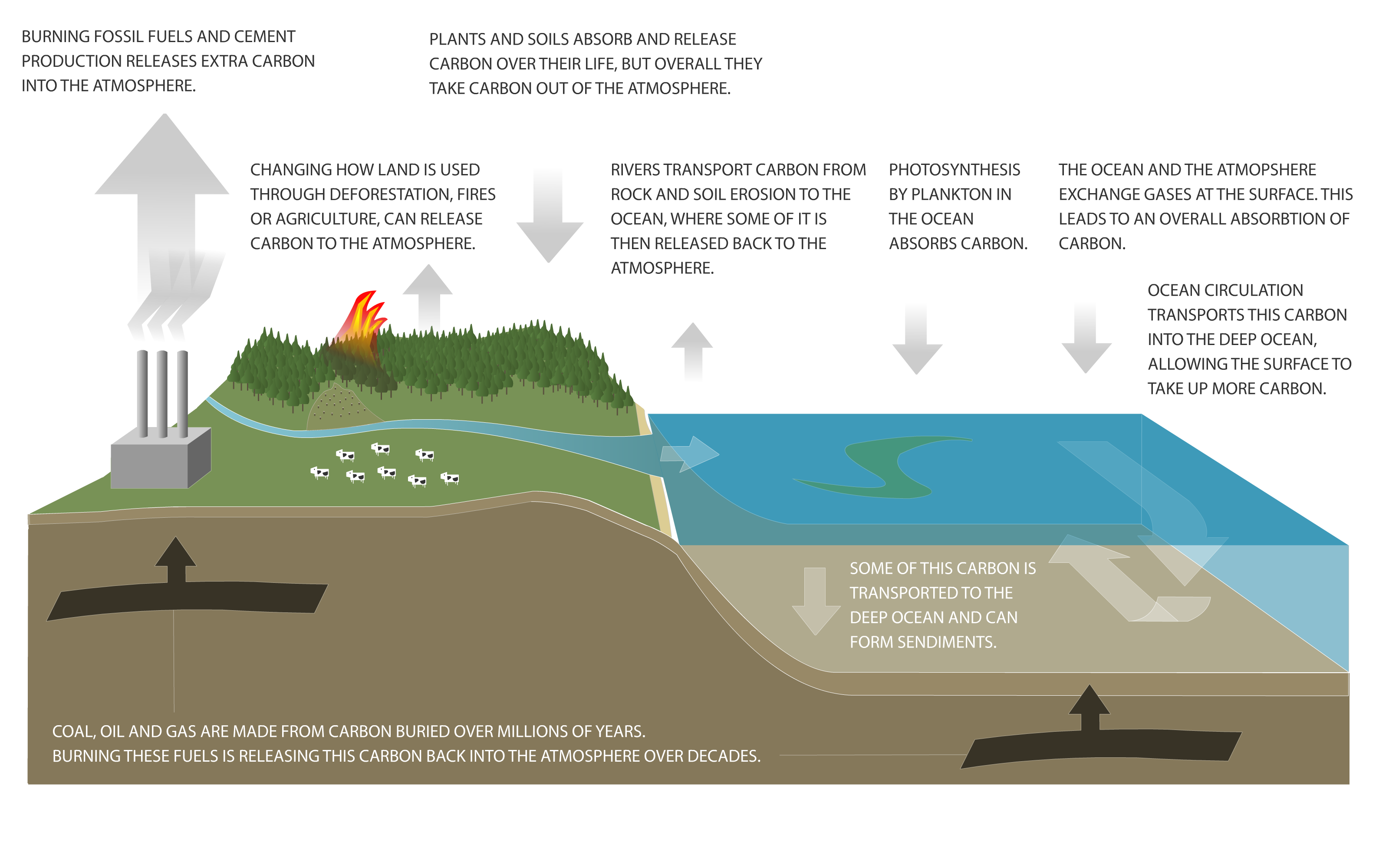
Comments
Post a Comment